Basic German Grammar Topics
-
German-Gender of Nouns4 Topics
-
German-Nominative4 Topics
-
German-Numbers4 Topics
-
German-Adjectives4 Topics
-
German-Personal Pronouns & the Verb sein4 Topics
-
German-Regular Verbs in the Present Tense4 Topics
-
German-Plural Formation4 Topics
-
German-Haben and the Accusative Case4 Topics
-
German-Word Order4 Topics
-
German-Definite Articles4 Topics
-
German-Indefinite Articles4 Topics
-
German-Negation5 Topics
-
German-Modal Verbs4 Topics
-
German-Separable Prefix Verbs4 Topics
-
German-Coordinating Conjunctions4 Topics
-
German-Konjunktiv I4 Topics
-
German-Possessive Pronouns4 Topics
-
German Question Words4 Topics
-
German-Present Perfect of Regular Verbs4 Topics
-
German-Present Perfect of Irregular Verbs4 Topics
-
German-Present Perfect of Mixed Verbs4 Topics
-
German-Dative Case5 Topics
-
German-Two Way Prepositions4 Topics
-
German-Dative Prepositions4 Topics
-
German-Conditionals4 Topics
-
German-Future Tense4 Topics
-
German-Dative Verbs4 Topics
-
German-Simple Past Tense4 Topics
-
German-Imperative4 Topics
-
German-Comparative4 Topics
-
German-Temporal Prepositions4 Topics
-
German-Present Perfect Separable Prefix Verbs4 Topics
-
German-Irregular Verbs4 Topics
-
German-Present Perfect Inseparable Prefix Verbs4 Topics
Participants 257
Lesson-German Separable Prefix Verbs
Stephen Sovenyhazy March 25, 2024
Learn how to use the separable prefix verbs in German (also known as “trennbare Verben”). We explain when to separate the prefix from a German verb and when not to. Get a list of the separable prefixes.
Verbs with a separable prefix (trennbare Verben)
Some verbs in German have a prefix attached to the verb stem. In some cases the prefix is not separable (untrennbare Verben), and in some cases, the prefix separates from the verb and moves to the end of the sentence, and the conjugated second part of the verb (the stem or root) is in the second position of the sentence.
In some cases, the prefix adds a more detailed meaning to the verb. For example, the verb “gehen” means “to go”, and the verb “weggehen” means “to go away” or to go out”. In other cases, adding a prefix changes the meaning of the verb quite a bit. For example, the verb “fallen” means “to fall”, but “einfallen” can mean “to come to mind”.
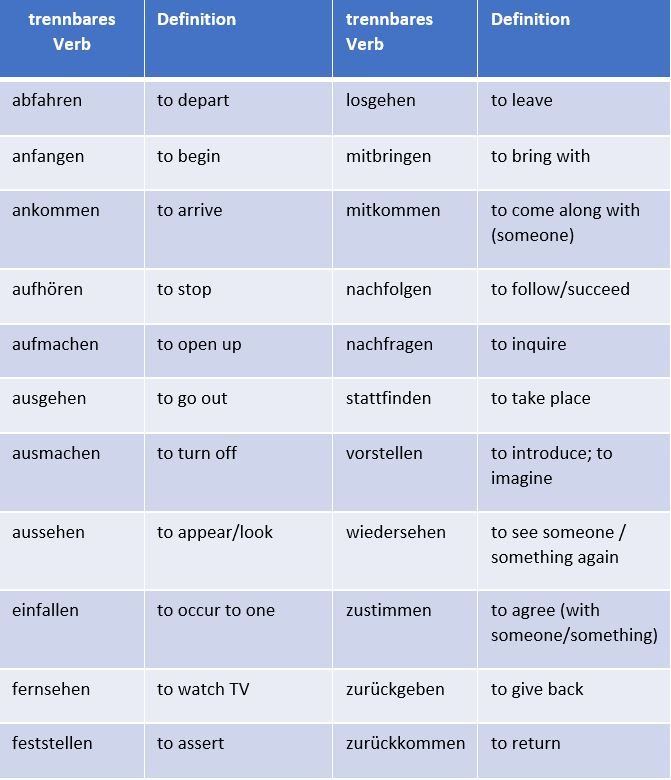
The most common separable prefixes in German are:
ab-, an-, auf-, aus-, bei-, da-, durch-, ein-, fern-, fest-, fort-, her-, hin-, mit-, nach-, um-, vor-, wieder-, zu-, and zurück-.
Examples (Beispiele)
einkaufen (to shop for groceries) – Ich kaufe im Supermarkt ein.
I shop for groceries at the supermarket.
anrufen (to call on the phone) – Er ruft Sabine an.
He calls Sabine on the phone. aufstehen (to get up) – Wir stehen um 6 Uhr auf.
We get up at 6 o’clockzurückfahren (to drive back) – Wir fahren heute Abend zurück.
We drive back this evening.
In dependent word order (e.g. in relative or subordinate clauses), the prefix rejoins its verb at the end of the dependent clause (see the fourth example below).
Separable prefix verbs with modal verbs or in dependent word order
When a separable prefix verb appear in a sentence with german modal verbs, the prefix rejoins the verb at the end of the sentence.
Example:
Ich rufe Bernd an. (I call Bernd on the phone.)
Ich muss Bernd anrufen. (I must call Bernd on the phone.)
When separable prefix verbs appear in a subordinate clause (dependent word order), the prefix also rejoins its verb at the end of the dependent clause.
Examples:
Er fährt heute weg. (He drives away/leaves today.)
Ich weiss nicht, ob er heute wegfährt. (I don’t know if he drives away/leaves today.)
Separable Prefix verbs in the present perfect
When separable prefix verbs are used in the present perfect (das Perfect), then the syllable “ge-“, which is usually placed in front of the participle for most verbs, is placed in between the separable prefix, and the verb stem.
Examples:
Ich sehe ihn. (I see him) -> Ich habe ihn gesehen. (I have seen him)
Ich sehe fern. (I watch TV) -> Ich have ferngesehen. (I have watched TV)
There are both regular and irregular separable prefix verbs. Here is a list of some common separable prefix verbs in German: